Calculer une expression littérale en donnant une valeur à la variable
Exemple 1
A = 2(3 − x) + x(5 + x)
• Pour calculer la valeur de A pour x = −2, il faut remplacer x par −2 puis effectuer les calculs.
A = 2(3 − (−2)) + (−2)(5 + (−2))
A = 2 × 5 + (−2) × 3
A = 10 − 6
A = 4
• On calcule de même la valeur de A pour x = 0.
A = 2(3 − 0) + 0(5 + 0)
A = 2 × 3 + 0
A = 6
Exemple 2
B = −3x2 + 5x + (x − 3)2
Pour calculer la valeur de B pour x = −2, il faut remplacer x par −2 sans oublier les parenthèses et les signes × sous-entendus.
B = −3 × (−2)2 + 5 × (−2) + (−2 − 3)2
B = −3 × 4 − 10 + (−5)2
B = −12 − 10 + 25
B = 3
Exercice n°1
Soit A = (5x − 10) + 2(5 − x).
Calcule A pour les valeurs suivantes de x.
Calcule A pour les valeurs suivantes de x.
Écrivez les réponses dans les zones colorées.
1. Pour x = 2, A = .
2. Pour x = 0, A = .
3. Pour x = −3, A = .
4. Pour x = −1, A = .
5. Pour x = 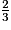 , A = .
, A = .
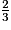 , A = .
, A = . 1. x = 2
A = (10 − 10) + 2 × 3
A = (10 − 10) + 2 × 3
3. x = −3
A = (− 15 − 10) + 2 × (5 + 3)
A = (− 15 − 10) + 2 × (5 + 3)
5. x = 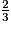
A =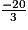 + 2 ×
+ 2 × 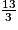
A =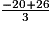
A =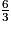
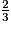
A =
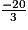 + 2 ×
+ 2 × 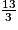
A =
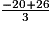
A =
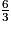
Exercice n°2
Calcule A et B pour différentes valeurs de x.
Écrivez les réponses dans les zones colorées.
1. Soit A = 5x2 − x + 2.
Pour x = 2, A = .
Pour x = −3, A = .
Pour x = 2, A = .
Pour x = −3, A = .
2. Soit B = −3x2 − x + 5.
Pour x = 1, B = .
Pour x = −2, B = −.
Pour x = 1, B = .
Pour x = −2, B = −.
1. x = 2
→ A = 5 × 4 − 2 + 2
x = −3
→ A = 5 × 9 + 3 + 2
→ A = 45 + 5
→ A = 5 × 4 − 2 + 2
x = −3
→ A = 5 × 9 + 3 + 2
→ A = 45 + 5
2. x = 1
→ B = −3 × 1 − 1 + 5
→ B = −3 − 1 + 5
x = −2
→ B = −3 × 4 + 2 + 5
→ B = −12 + 2 + 5
→ B = −3 × 1 − 1 + 5
→ B = −3 − 1 + 5
x = −2
→ B = −3 × 4 + 2 + 5
→ B = −12 + 2 + 5
Exercice n°3
Coche la bonne réponse.
a. Calcule A lorsque x = 4.
A = 5x2 − 0,5x + 3
A = 5x2 − 0,5x + 3
Cochez la bonne réponse.
| ||
| ||
| ||
|
b. Calcule B lorsque x = −3.
B = 3x (12 − 2x)
B = 3x (12 − 2x)
Cochez la bonne réponse.
| ||
| ||
| ||
|
a. On calcule :
A = 5 × 42 − 0,5 × 4 + 3 = 5 × 16 − 2 + 3
A = 80 − 2 + 3 = 78 + 3 = 81
A = 5 × 42 − 0,5 × 4 + 3 = 5 × 16 − 2 + 3
A = 80 − 2 + 3 = 78 + 3 = 81
Exercice n°4
Coche la bonne réponse.
a. Calcule A lorsque x = 102.
A = x2 +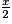
A = x2 +
Cochez la bonne réponse.
| ||
| ||
| ||
|
b. Calcule B lorsque x = −7.
B =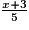
B =
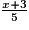
Cochez la bonne réponse.
| ||
| ||
| ||
|

